E-Invoicing in Malaysia
Last update: 2026, January 7
Summary
B2G, B2B, B2C
Mandatory
E-Invoicing is currently mandatory all companies in Malaysia with a turnover above RM 1 million (~200 K€) through the central platform MyInvois following a Clearance model.
What the Law Says
Countrywide E-Invoicing Mandate
The government of Malaysia, by the intermediary of its tax authority, the IRBM (Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia) has gradually implemented an e-invoicing mandate that applies to all types of transactions (B2G, B2B and B2C).
The mandate entered into effect depending on companies revenue, between August 1, 2024 and January 1, 2026, and now applies countrywide for all companies exceeding RM 1 million annual turnover (~200K€).
Under this mandate, suppliers must submit all invoices to the MyInvois central platform, either manually via a web interface or automatically through an API in UBL 2.1 format (XML or JSON).
Once the invoice content is verified, the MyInvois platform validates it and generates an e-invoice with a Unique Identifier Number (UIN) and a PDF version of the invoice with a QR code. The supplier is then responsible for delivering either (or both) to the buyer through their preferred channel.
Regarding the invoice delivery topic, the Malaysian government, through the Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC), is driving a national e-invoicing initiative that primarily encourages the use of the Peppol network and the Malaysian Peppol International (MY PINT) invoice format.
All validated e-invoices will also be automatically archived by the IRBM and accessible through the MyInvois platform.
Grace Period & Exemptions
In the first six months of implementing the e-invoicing mandate, each taxpayer group in the rollout will be allowed a grace period and will be permitted to issue consolidated e-invoices on a monthly basis, rather than issuing a separate e-invoice for each transaction.
Additionally, as described in the official guidelines, the mandate only applies to private companies, as the public sector seems exempted from issuing e-invoices for the time being.
Finally, the mandate will not apply to very small companies (annual revenue below RM 1 million (~200K€), as announced by the government a few days before the start of the first phase of the mandate. It has been confirmed in version 3.2 of the guidelines, and in the official FAQ.
Other Methods
For small businesses not impacted by the e-invoicing mandate, e-invoicing via the MyInvois central platform is possible using the same rules, while traditional methods also remain allowed:
- Paper-based invoices
- PDF invoices with e-signature or complete audit trail
- EDI
All invoices must be archived for 7 years.
Timeline
E-Invoicing Mandatory - Large Companies
Large companies (turnover > RM 100M) must send electronic invoices through the MyInvois central platform
E-Invoicing Mandatory - Mid-size Companies
The e-invoicing mandate starts applying to medium-sized companies (turnover > RM 25M)
E-Invoicing Mandatory - Small Companies
The e-invoicing mandate starts applying to small companies (turnover > RM 5M)
E-Invoicing Mandatory - All Companies
All invoicing transactions must be performed in an electronic way through the MyInvois central platform, except for very small companies (turnover < RM 1M) for which the mandate does not apply.
Latest E-Invoicing News in Malaysia
Malaysia extends e-invoicing deadline for small businesses
Malaysia’s E-Invoicing mandate will apply to more businesses in 2025
Technical Details
The following technical details focus on the countrywide e-invoicing mandate. Comprehensive guidelines and a SDK (Software Development Kit) are also maintained by the IRBM, providing more ample information.
E-Invoice Validation
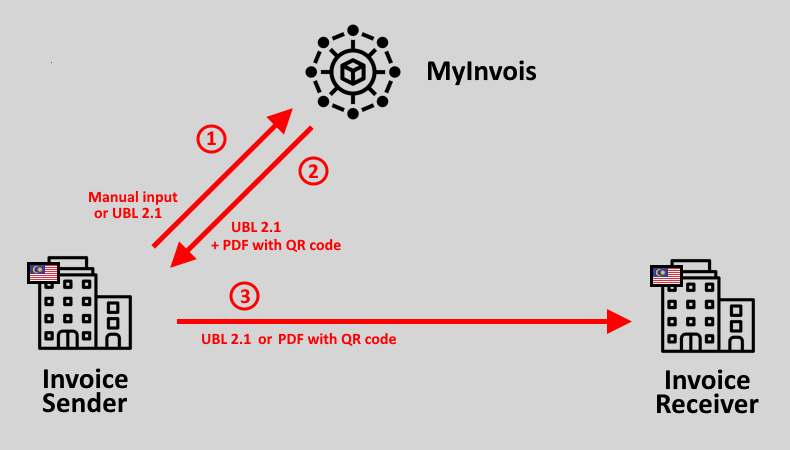
(Steps 1 & 2 as illustrated in the schema above)
In Malaysia, all e-invoices must undergo validation by the tax authority through the MyInvois central platform before reaching their final recipient.
To submit an e-invoice to MyInvois, suppliers have two options:
- Manual data input via a web interface: this method is suitable for small volumes and companies without automated e-invoicing solutions (web interface guidelines are available)
- Automated submission via a REST API: e-invoices submitted this way must adhere to the UBL 2.1 standard, be formatted in either XML or JSON, and digitally signed.
Once validated by MyInvois, the supplier will receive an e-invoice containing a Unique Identifier Number (UIN) and a PDF version of the invoice containing a QR code.
Both the supplier and the buyer also get notified by MyInvois alerting them about the e-invoice.
E-Invoice Delivery
(Step 3 as illustrated in the schema above)
Upon validation by MyInvois, it becomes the supplier’s responsibility to ensure the invoice is delivered to the buyer. Both the supplier and the buyer are free to agree on their preferred delivery method.
Typically, most companies will opt to share the PDF invoice (with the QR code) via email. But the IRBM also strongly encourages sharing the e-invoice (in XML/JSON UBL 2.1 format) containing the UIN through the Peppol network, in order to maximize the benefits of e-invoicing, such as streamlining operations and reducing manual processing through automation.
The UIN and/or the QR code then enable the buyer to verify the validity of the e-invoice on MyInvois.
Furthermore, there is a 72-hour window after the invoice validation for the supplier to cancel the invoice or for the buyer to reject it. As the buyer received a notification from MyInvois upon validation of the e-invoice, they are aware that they should expect to receive an e-invoice from their supplier very soon.
National E-Invoicing Initiative (via Peppol)
In addition to the e-invoicing mandate primarily aimed at tax reporting, the Malaysian government is promoting a (non-mandatory!) national e-invoicing initiative through the Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC), which has published official guidelines. This voluntary program encourages companies to adopt e-invoicing to leverage the numerous benefits of automation, such as faster processes and fewer manual errors.
Relying on the Peppol network, service providers wanting to offer Peppol services in Malaysia must be certified by the MDEC, which maintains lists of certified Peppol Service Providers and certified Peppol-Ready Service Providers are maintained. All Peppol requirements are also detailed in the Peppol Authority Specific Requirements for Malaysia.
Using the Malaysian version of the Peppol International (MY PINT) format, this initiative also allows compatibility with the e-invoicing mandate. The Peppol service provider of the invoice sender can indeed ensure compliance by sending the required data (in UBL 2.1 format) to the MyInvois portal, retrieving the UIN, and sending a MY PINT e-invoice via Peppol to the recipient.
Cross-Border Invoices
Foreign companies do not have to comply with the mandate. Rather, this responsibility falls upon the Malaysian company.
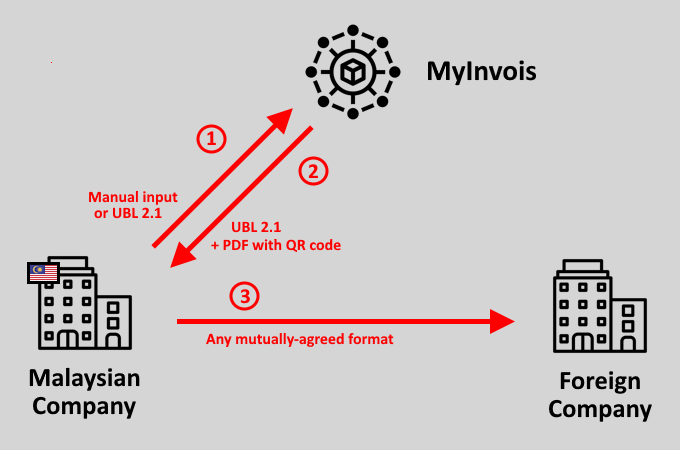
Sending Cross-Border Invoices
Sending cross-border invoices will not differ significantly from sending domestic invoices for a Malaysian company.
When a Malaysian seller invoices a foreign buyer, they must follow the mandated process by validating their e-invoice through MyInvois (steps 1 & 2) and must then send a copy of the invoice to the foreign buyer in a mutually agreed format (step 3).
The only difference stands in the fact that Malaysian businesses are not required to use the e-invoice or the PDF with QR code generated by MyInvois for foreign transactions. They can rather use the mutually agreed-upon format & channel with their foreign buyer.
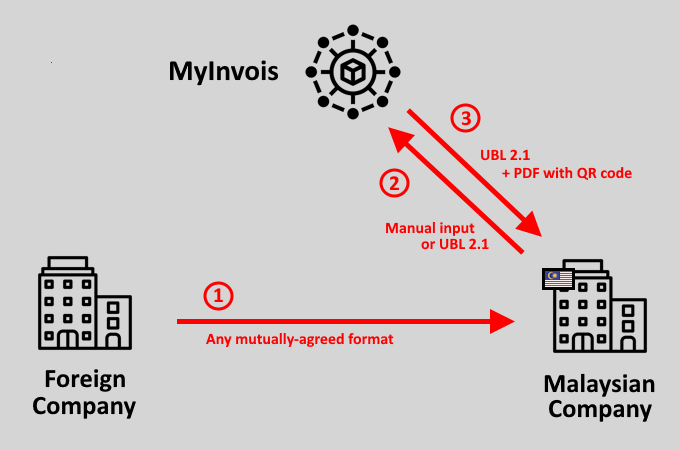
Receiving Cross-Border Invoices
Receiving cross-border invoices introduces a bit more complexity for the Malaysian company.
When a foreign seller invoices a Malaysian buyer, the foreign seller is free to issue the invoice as they see fit (step 1).
Then, the Malaysian buyer must subsequently issue a corresponding self-invoice and submit this self-invoice to MyInvois for validation (steps 2 & 3).
Invoice Archiving
All e-invoices validated by the MyInvois platform are automatically archived by the IRBM.
Suppliers and buyers then have the ability to retrieve those invoices in various formats, either using MyInvois web interface or via its API:
- E-invoice (XML or JSON format)
- Metadata
- PDF invoice (via web interface only)
- Grid (via web interface only)
The Invoicing Hub Word
Malaysia
Malaysia is adopting a pre-clearance e-invoicing mandate akin to those in effect in Latin America.
Under this approach, suppliers must initially validate their invoices through the MyInvois central platform, which then generates e-invoice and PDFs containing validation proofs. Suppliers are then free to send those verified invoices through their usual channels.
While this type of mandate reduces project scale as the actual delivery of the invoice is not in scope, it falls short in harnessing the full potential of e-invoicing, likely offering minimal automation benefits.
Nevertheless, Malaysia emerges as a pioneering nation in the Asia-Pacific region to enact a comprehensive e-invoicing mandate, setting a precedent for others to follow suit.
Moreover, the Malaysia tax authority offers clear guidelines, detailed use cases, and comprehensive technical documentation, thus easing the burden for companies falling under the mandate’s scope.
Additional Resources
Public entity in charge of e-invoicing in Malaysia
Guidelines & technical specifications maintained by the IRBM
MyInvois is part of the MyTax portal
Comprehensive set of technical resources to interact with the MyInvois platform
Peppol Authority in Malaysia
Guidelines, certified providers & technical specifications for the use of Peppol in Malaysia
Get your Project Implemented
Gold Sponsor
Silver Sponsors
Latest News
The French e-invoicing pilot begins, alongside updates to AFNOR standards
Greece’s B2B mandate to start one month late, on March 2
Peppol G2 to G3 certificate migration on April 1st 2026
E-Invoicing Compliance in the UAE: The Complete Guide
Sweden to assess implementation of domestic e-invoicing
📩 Newsletter
Receive the latest e-invoicing news, directly in your mailbox, once a month.